 400-076-6558智领未来,外贸超级营销员
400-076-6558智领未来,外贸超级营销员
 400-076-6558智领未来,外贸超级营销员
400-076-6558智领未来,外贸超级营销员

In the competitive landscape of global B2B trade, traditional keyword-based buyer searches often fall short, producing vague leads with uncertain procurement intent. However, the advent of integrating customs import-export data combined with strategic analysis of HS codes and purchase frequency metrics is revolutionizing how exporters identify and engage high-potential overseas buyers. This methodology helps exporters sift through millions of transaction records to build authentic buyer profiles, dramatically enhancing lead quality and conversion rates.
Global customs data is a publicly accessible yet highly structured source comprising shipment manifests, declared product categories, trade volumes, and counterparties. Derived from millions of international cross-border transactions annually, this data is gathered and standardized by government customs agencies globally. Its legal acquisition ensures compliance with international trade regulations, making it a goldmine for digital-savvy export businesses aiming to replace guesswork with data-driven decisions.
Harmonized System (HS) codes are internationally standardized product classification codes dividing goods into detailed categories. Leveraging HS codes allows exporters to filter buyers according to specific product groups, ensuring precision targeting rather than broad interest signals. Purchase frequency, or how often a buyer imports said HS-coded products over defined timeframes, signals the reliability and seriousness of their procurement needs.
For example, a purchasing entity importing electronic components (HS code 8542) monthly at scale over a year demonstrates sustained buying intent, drastically lowering cold-lead risks. This dual filter—HS code + purchase frequency—enables exporters to differentiate steady, high-potential buyers from one-off or speculative ones, a critical advancement over traditional keyword searches that may capture mere browsing interest.
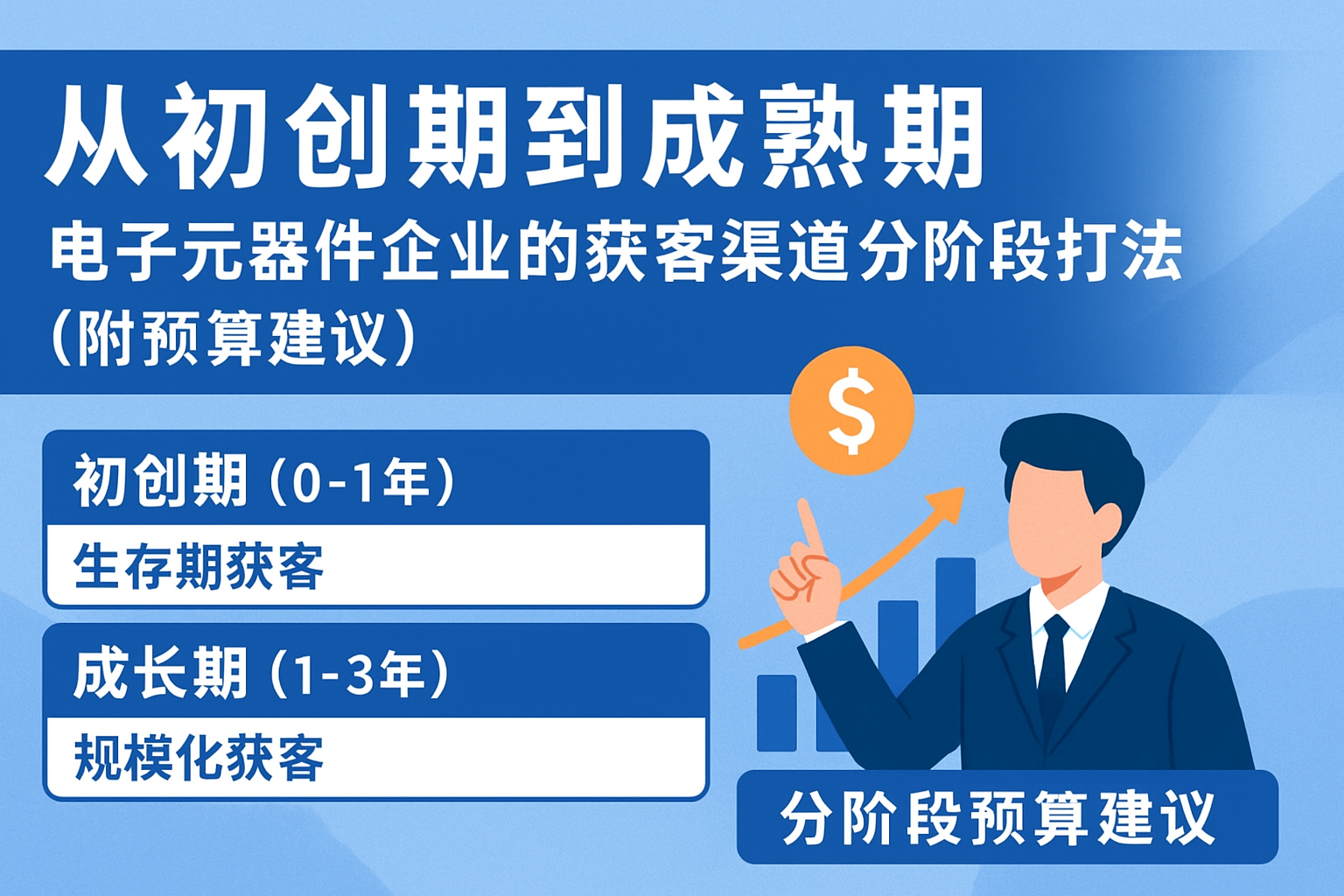
Constructing robust buyer personas using customs data involves integrating several key fields: HS codes, purchase frequency, trade volume, shipment locations, and buyer/company metadata. Analytical tools harness AI-powered algorithms to cluster buyers by industry, order recurrence, and geographic footprint, revealing authentic procurement patterns.
The process includes:
Different B2B sectors show unique procurement behaviors reflected in customs data:
Tailoring threshold parameters in HS code and frequency filters by sector elevates lead qualification accuracy and prevents resource wastage on low-fit prospects.
.jpg)
1. Data Acquisition: Partner with reputable customs data providers offering real-time or periodic data feeds covering target markets.
2. HS Code Analysis: Define core product HS codes linked to your export offerings.
3. Frequency Threshold Setting: Set minimum purchase frequency (e.g., ≥ 3 imports in 6 months) and trade volume filters to identify serious buyers.
4. Buyer Profiling: Enrich leads by cross-referencing company registration details, shipment destinations, and historical trade values.
5. Multilingual Monitoring: Use AI-powered language analysis tools to detect buyer communications in various languages, improving lead understanding.
6. Integration with CRM: Seamlessly import qualified leads into CRM systems to design personalized outreach campaigns.
Deploying these steps can reduce cold-lead ratio by over 40%, while increasing lead-to-opportunity conversion by upwards of 25% within 4 months of implementation, based on field data from multiple B2B exporters.

Conventional methods relying on keyword searches or trade fair leads tend to generate low-quality and uncertain-intent prospects, leading to wasted sales effort. In contrast, leveraging customs data provides:
“Click here to discover how to swiftly screen and engage high-potential overseas buyers using customs data” — transform your B2B lead sourcing with precision and confidence.
.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,h_100,m_lfit/format,webp)
.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,h_100,m_lfit/format,webp)

.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,h_100,m_lfit/format,webp)
.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,h_100,m_lfit/format,webp)
.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,h_100,m_lfit/format,webp)
.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,h_100,m_lfit/format,webp)
